Configure Linux Server as Router with Dynamic BGP (part 1)
Recently I need to test BGP settings of a router. However I do not have operate permission on the upstream router. Therefore I decided to add a Linux router between. This article introduces how to set up a linux router with dynamic BGP.
Step 1: Topology
Without the Linux router, the children router connects to upstream router directly.
Upstream router (10.0.x.1)
-> children router (10.0.x.x, 192.168.x.1)
-> VMs (192.168.x.x)
With the new Linux router, the children routers connects to upstream router via the new Linux router.
Upstream router (10.0.x.1)
-> new Linux router (10.0.x.x, 10.200.0.1)
-> children router (10.200.0.x, 192.168.x.1)
-> VMs (192.168.x.x)
Step 2: Create a Linux server
At first create a Linux server from Ubuntu 24.04 cloud image. The server has two NICs:
- Default NIC: eth0/ens35 (10.0.x.x)
- Second NIC: eth1/ens36 (10.200.0.1, it will be used as gateway of children routers)
The netplan is configured as below
root@test-router:~# cat /etc/netplan/50-cloud-init.yaml
network:
ethernets:
ens35:
dhcp4: true
ens36:
dhcp4: false
addresses:
- 10.200.0.1/24
- fc00:2024:9:7::1/64
version: 2
After running netplan apply, the IPs are configured
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 1e:00:c7:00:01:38 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
altname enp2s3
altname ens35
inet 10.0.XX.XX/20 metric 100 brd 10.0.47.255 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::1c00:c7ff:fe00:138/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: eth1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 02:00:3e:61:00:01 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
altname enp2s4
altname ens36
inet 10.200.0.1/24 brd 10.200.0.255 scope global eth1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fc00:2024:9:7::1/64 scope global
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::3eff:fe61:1/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Step 3: Setup Linux server as a router
The Linux server can be setup as a router very easily by the following commands.
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
sudo iptables -F
sudo iptables -X
sudo iptables -t nat -F
sudo iptables -t nat -X
sudo iptables -t mangle -F
sudo iptables -t mangle -X
sudo iptables -P INPUT ACCEPT
sudo iptables -P OUTPUT ACCEPT
sudo iptables -P FORWARD ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A FORWARD -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -j MASQUERADE
The last rule (MASQUERADE) can be replaced by
sudo iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j SNAT --to-source 10.0.XX.XX
Step 4: Verify routing
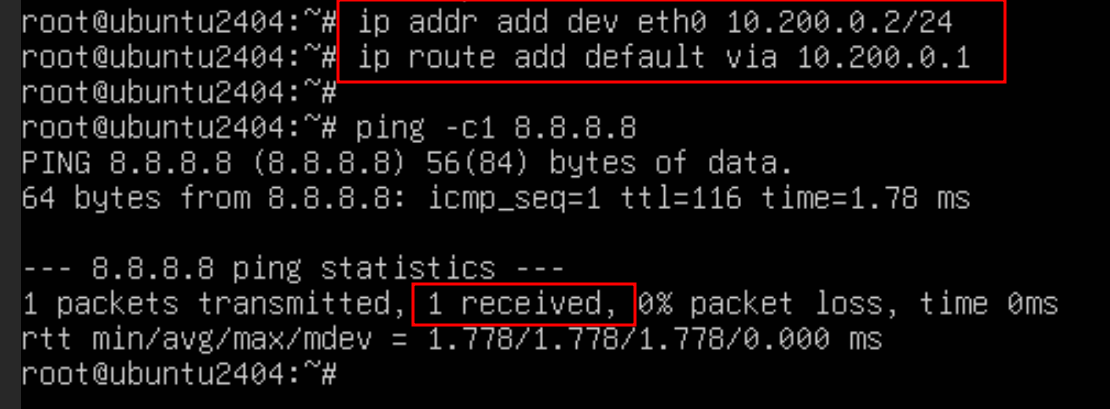
Now deploy a test server on the same network as the Linux router.
After configuring the IP/gateway and default route, the test server can reach the internet.
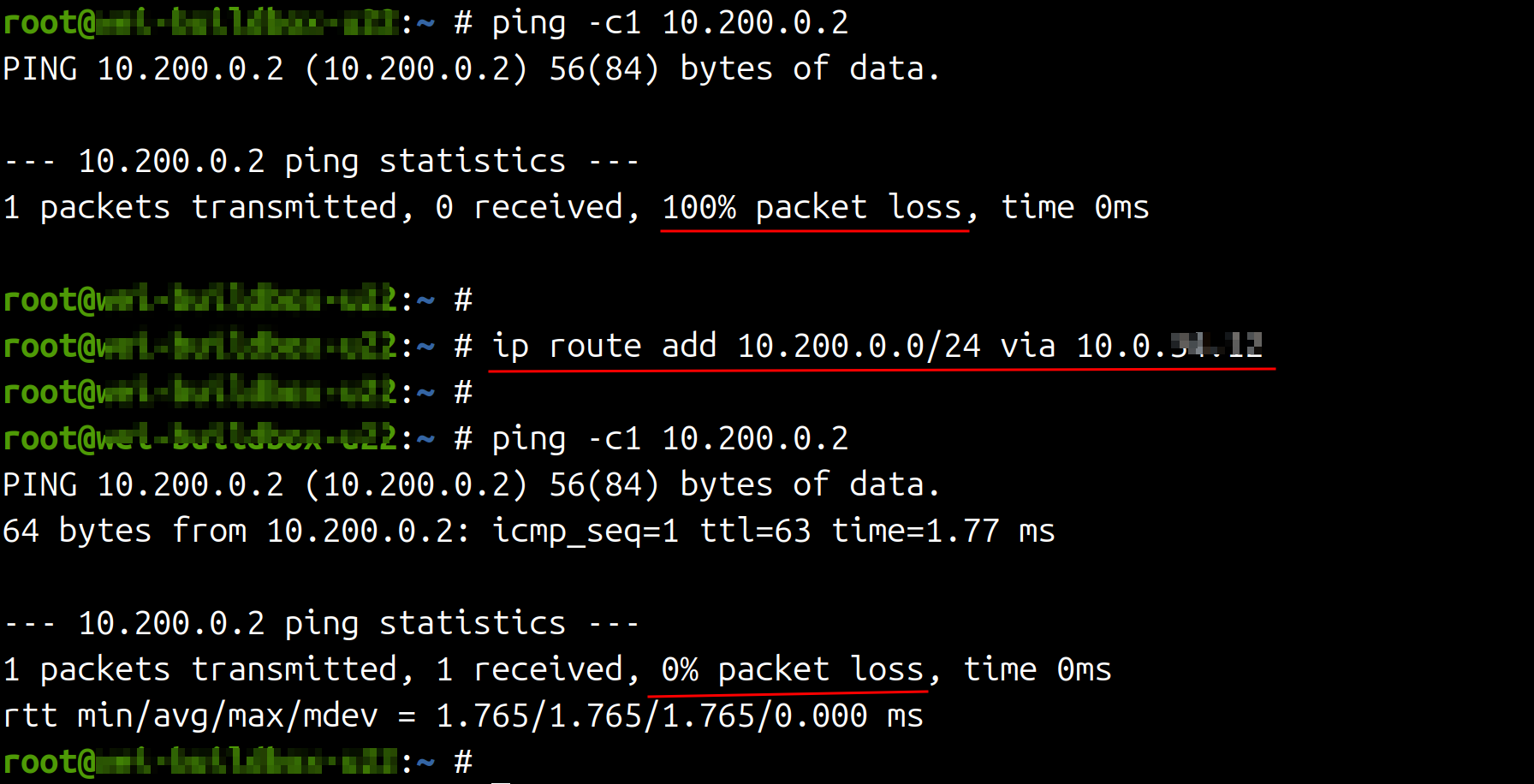
To reach the test server from other servers, a route needs to be added in the source host (on same network) or the upstream router (otherwise).