Mastering SAN in CloudStack (Part 3 - Add OCFS2 as SharedMountPoint Storage Pool)
KVM supports “Shared Mountpoint” storage. A shared mountpoint is a file system path local to each server in a given cluster. The path must be the same across all Hosts in the cluster, for example /mnt/primary1. This shared mountpoint is assumed to be a clustered filesystem such as OCFS2. In this case the CloudStack does not attempt to mount or unmount the storage as is done with NFS. The CloudStack requires that the administrator insure that the storage is available.
In this part, we will introduce how to use OCFS2 in Apache CloudStack.
Add OCFS2 as SharedMountPoint Storage Pool
To add a storage pool:
- Log in to the CloudStack UI as an administrator.
- In the left navigation bar, click Infrastructure -> Primary Storage.
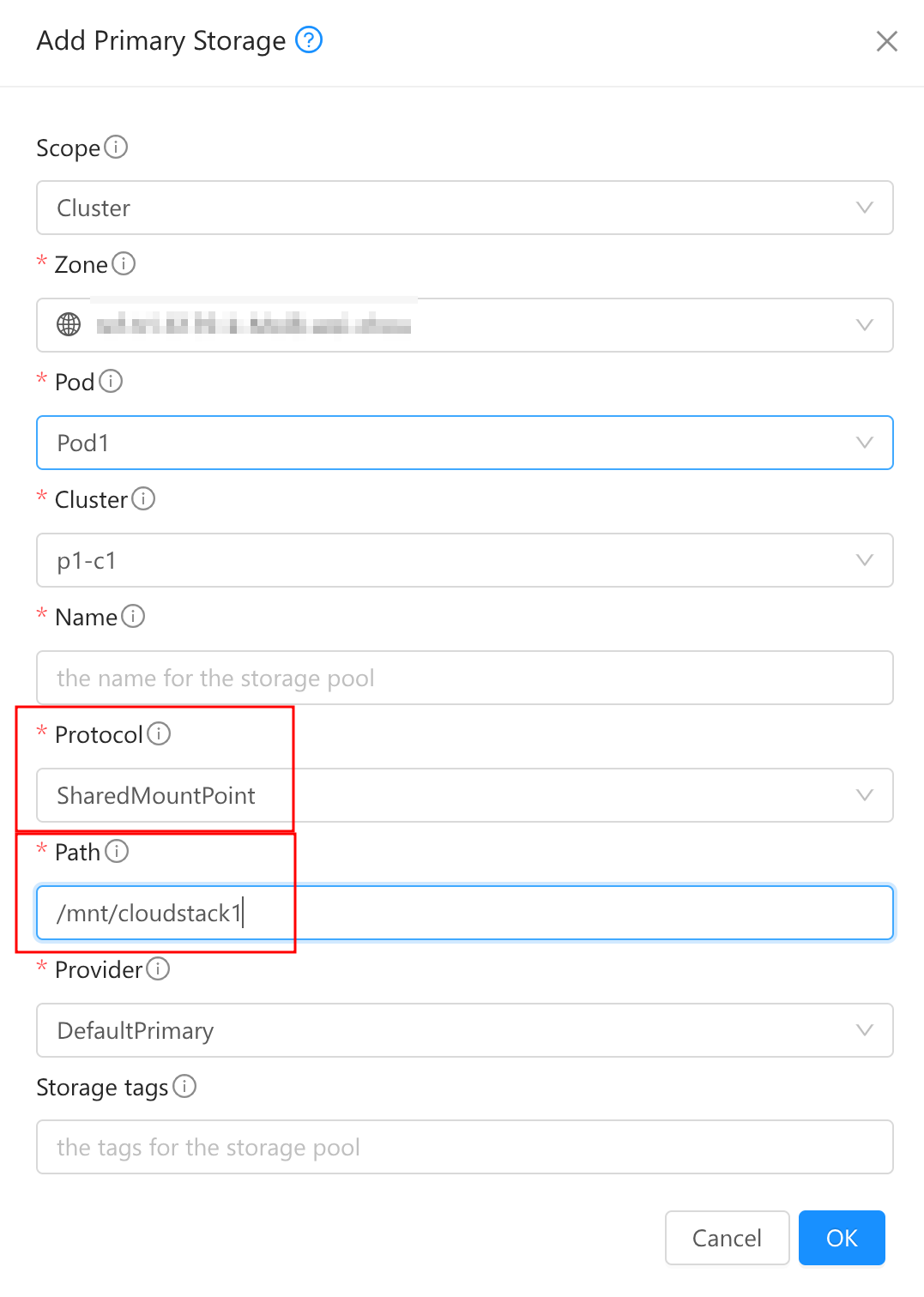
- Click “Add Primary Storage”.
In the dialog box, fill in the following fields:
- Scope. Choose “Zone” or “Cluster”
- Name. Give the name for the storage pool
- Protocol. Choose
SharedMountPoint - Path. For SharedMountPoint,where primary storage is mounted, such as
/mnt/cloudstack1or/mnt/cloudstack2 - Provider. Choose
DefaultPrimary - Storage tags (optional). Give the tags for the storage pool.
Add both OCFS2 in CloudStack,

Supported Operations
The SharedMountPoint is expected to work as the similar way as NFS. Many VM or Volume operations should work.
VM Operations
- Deploy VM
- Start/Stop/Migrate
- Destroy/Expunge VM
- Migrate VM from a SharedMountPoint to another SharedMountPoint
- Scale VM
- VM Snapshotting
Volume Operations
- Create Volume
- Attach Volume to VM
- Detach volume from VM
- Delete Volume
- Migrate Volume of Stopped VM from a SharedMountPoint to another SharedMountPoint
- Resize Volume
- Volume Snapshotting (Internal and External)
Operations to be verified
- Migrate VM between a SharedMountPoint to a NFS
- Migrate Volume of Stopped VM between a SharedMountPoint to a NFS
- Import/Unmanage Volume
